Getting Started¶
Citus Cloud is a fully managed hosted version of Citus Enterprise edition on top of AWS. Citus Cloud comes with the benefit of Citus allowing you to easily scale out your memory and processing power, without having to worry about keeping it up and running.
Provisioning¶
Once you’ve created your account at https://console.citusdata.com you can provision your Citus cluster. When you login you’ll be at the home of the dashboard, and from here you can click New Formation to begin your formation creation.
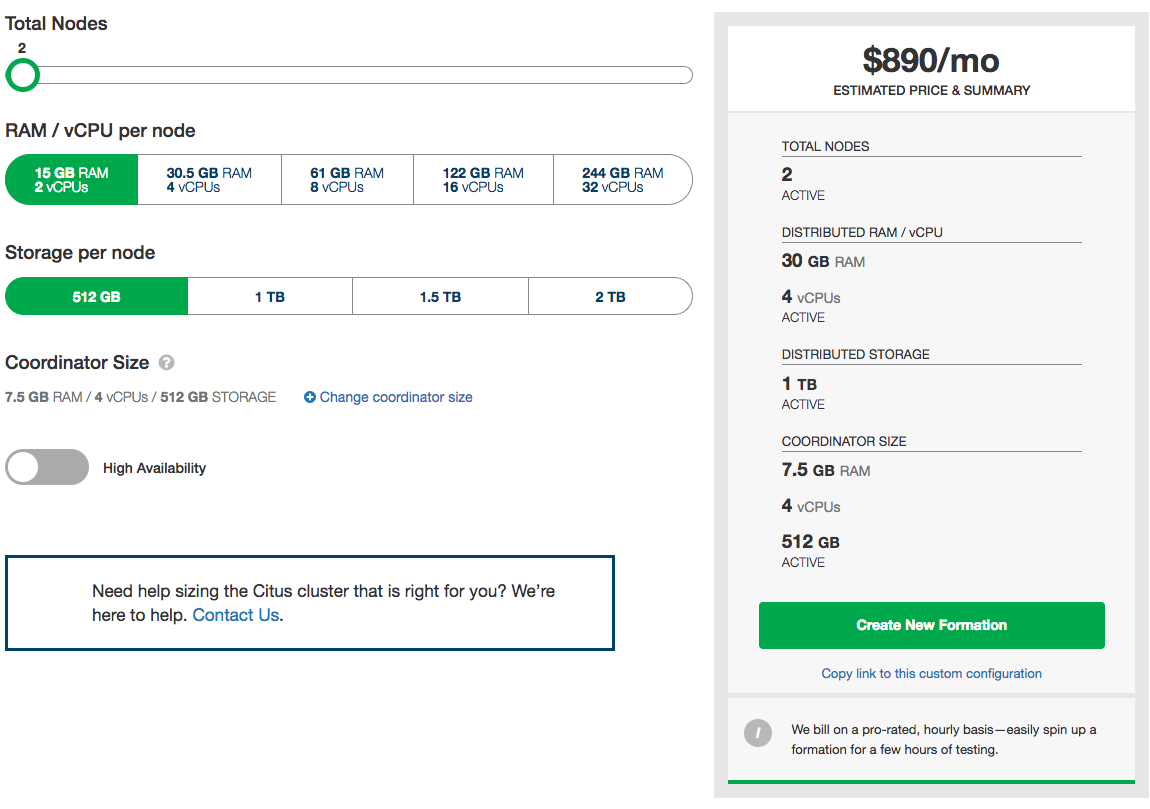
Configuring Your Plan¶
Citus Cloud plans vary based on the size of your primary node, size of your distributed nodes, number of distributed nodes and whether you have high availability or not. From within the Citus console you can configure your plan or you can preview what it might look like within the pricing calculator.
The key items you’ll care about for each node:
- Storage - All nodes come with 1 TB of storage
- Memory - The memory on each node varies based on the size of node you select
- Cores - The cores on each node varies based on the size of node you select
Supported Regions¶
Citus Cloud runs on top of Amazon Web Services. During provisioning you’re able to select your database region. We currently support:
- US East (N. Virginia) [us-east-1]
- US East (Ohio) [us-east-2]
- Asia Pacific (Tokyo) [ap-northeast-1]
- Asia Pacific (Seoul) [ap-northeast-2]
- Asia Pacific (Singapore) [ap-southeast-1]
- Asia Pacific (Sydney) [ap-southeast-2]
- Asia Pacific (Mumbai) [ap-south-1]
- EU (Frankfurt) [us-central-1]
- EU (Ireland) [us-west-1]
- South America (São Paulo) [sa-east-1]
- US West (N. California) [us-west-1]
- US West (Oregon) [us-west-2]
If there is an AWS region you do not see listed but would like for us to add support for please contact us and we’d be happy to look into it.
Other infrastructure providers¶
At this time we only support Citus Cloud on top of Amazon Web Services. We are continually exploring other infrastructure providers to make Citus Cloud available on. If you have immediate needs you could consider running Citus Community Edition or Citus Enterprise Edition. Or if you have questions about our timeline for other infrastructure providers please feel free to reach out.
Connecting¶
Applications connect to Citus the same way they would PostgreSQL, using a connection URI. This is a string which includes network and authentication information, and has the form:
postgresql://[user[:password]@][host][:port][/dbname][?param1=value1&...]
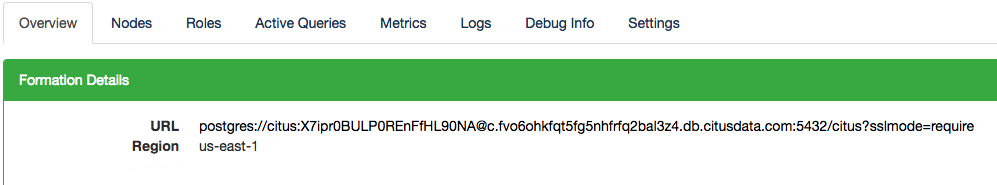
The connection string for each Cloud Formation is provided on the Overview tab in Citus Console.
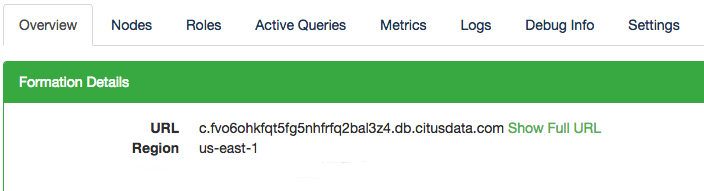
By default the URL displays only the hostname of the connection, but the full URL is available by clicking the “Show Full URL” link.
Support and Billing¶
All Citus Cloud plans come with support included. Premium support including SLA around response time and phone escalation is available on a contract basis for customers that may need a more premium level of support.
Support¶
Web based support is available on all Citus Cloud plans. You can open a support inquiry within the Citus Cloud console. Support response times for ticket classification of Citus Cloud are:
- Urgent (production database offline) - 1 hour response time
- High (production database impacted) - 4 hour response time
- Normal (general support) - 1 business day response time
- Low (general question) - 3 business days response time
Billing and pricing¶
Citus Cloud bills on a per minute basis. We bill for a minimum of one hour of usage across all plans. Pricing varies based on the size and configuration of the cluster. A few factors that determine your price are:
- Size of your distributed nodes
- Number of distributed nodes
- Whether you have high availability enabled, both on the primary node and on distributed nodes
- Size of your primary node
You can see pricing of various configurations directly within our pricing calculator.
Extensions¶
To keep a standard Cloud installation for all customers and improve our ability to troubleshoot and provide support, we do not provide superuser access to Cloud clusters. Thus customers are not able to install PostgreSQL extensions themselves.
Generally there is no need to install extensions, however, because every Cloud cluster comes pre-loaded with many useful ones:
| Name | Version | Schema | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| btree_gin | 1.0 | public | support for indexing common datatypes in GIN |
| btree_gist | 1.2 | public | support for indexing common datatypes in GiST |
| citext | 1.3 | public | data type for case-insensitive character strings |
| citus | 7.0-15 | pg_catalog | Citus distributed database |
| cube | 1.2 | public | data type for multidimensional cubes |
| dblink | 1.2 | public | connect to other PostgreSQL databases from within a database |
| earthdistance | 1.1 | public | calculate great-circle distances on the surface of the Earth |
| fuzzystrmatch | 1.1 | public | determine similarities and distance between strings |
| hll | 1.0 | public | type for storing hyperloglog data |
| hstore | 1.4 | public | data type for storing sets of (key, value) pairs |
| intarray | 1.2 | public | functions, operators, and index support for 1-D arrays of integers |
| ltree | 1.1 | public | data type for hierarchical tree-like structures |
| pg_buffercache | 1.2 | public | examine the shared buffer cache |
| pg_freespacemap | 1.1 | public | examine the free space map (FSM) |
| pg_prewarm | 1.1 | public | prewarm relation data |
| pg_stat_statements | 1.4 | public | track execution statistics of all SQL statements executed |
| pg_trgm | 1.3 | public | text similarity measurement and index searching based on trigrams |
| pgcrypto | 1.3 | public | cryptographic functions |
| pgrowlocks | 1.2 | public | show row-level locking information |
| pgstattuple | 1.4 | public | show tuple-level statistics |
| plpgsql | 1.0 | pg_catalog | PL/pgSQL procedural language |
| session_analytics | 1.0 | public | |
| shard_rebalancer | 7.0 | public | |
| sslinfo | 1.2 | public | information about SSL certificates |
| tablefunc | 1.0 | public | functions that manipulate whole tables, including crosstab |
| unaccent | 1.1 | public | text search dictionary that removes accents |
| uuid-ossp | 1.1 | public | generate universally unique identifiers (UUIDs) |
| xml2 | 1.1 | public | XPath querying and XSLT |

